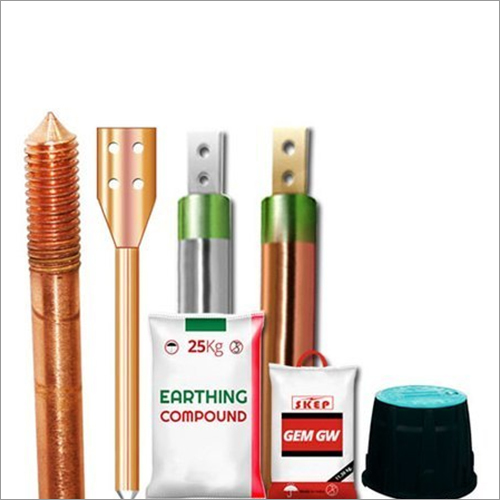
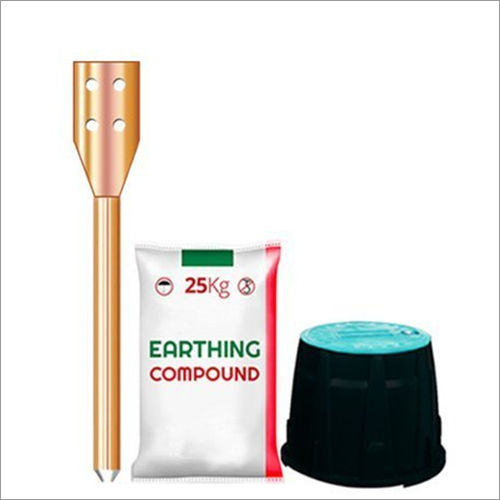
Earthing Electrodes for Homes
Product Details:
- Product Type Earthing Electrode
- Application Maintenance Free Chemical Earthing
- Click to View more
Earthing Electrodes for Homes Price And Quantity
- 1 Set
- 4500 INR/Set
Earthing Electrodes for Homes Product Specifications
- Maintenance Free Chemical Earthing
- Earthing Electrode
Earthing Electrodes for Homes Trade Information
- 100 Set Per Month
- 24 Hours
Product Description
Earthing refers to transmitting electrical discharges from the device to the ground using cables or low resistance wires. An electrical charge shared directly with the earth is known as earthing. Electrical damage and malfunctions can be prevented by earthing the device and power system. Earthing is mainly used to reduce overload on electrical systems.
The main essential features of an earthing system, include:
- User protection against electrical shock by blowing fuse.
- The system ensures electrical appliance's conductive parts must continue to work up to their potential, and do not reach beyond their potential.
- The earthing system creates a safe conductive path for dissipating short circuit current.
- Prevents excessive current or voltage from flowing through any part of an electrical system.
Apart from using earthing electrodes for homes, the professionals install them in steel plant, power plant, cement plant, etc. These electrodes play an essential role in underground and overhead electricity distribution and transmission networks. The professionals make proper consideration while making selection of right earthing electrode so that save path is paved for electrical faults, and fault current is efficiently dissipated to prevent any kind of damage or downtime to electric equipment.
An earthing electrode is easy to install, requires less space and lasts longer than conventional earthing. A conductive and hygroscopic powder is used around the earthing electrode for home to make sure it prolongs the effective earthing period. It is known that the powder absorbs and retains moisture for long period of time. An earthing system with a low resistance values ensure safety and soundness.
Characteristics Of Earthing Electrodes :
- tensile strength
- Perfect execution
- Long-lasting
Application Of Earthing Electrodes:
- Industries in Heavy
- nuclear, LNG, and petrochemical facilities
- Automation and process management
- Banks, ATMs, clinics, railroads, airports, and military and defence facilities.
Technical Specifications:
| Lengths | OD ISI GI | ISI GI PIPE | Technical Details | ||
| Outer | Inner | Copper Terminal | Outer Pipe Thickness | Inner Pipe Thickness | |
| 3.0 meter | 300 cm x 90 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm x 6 mm | 14 gauge | 12 gauge |
| 2.0 meter | 200 cm x 90 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm x 6 mm | 14 gauge | 12 gauge |
| 1.5 meter | 150 cm x 90 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm x 6 mm | 14 gauge | 12 gauge |
| 1.0 meter | 100 cm x 50 mm | 25 mm | 25 mm x 3 mm | 14 gauge | 12 gauge |
Other Products in 'Chemical Earthing Set' category
 |
ELAPP POWER PRIVATE LIMITED
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |